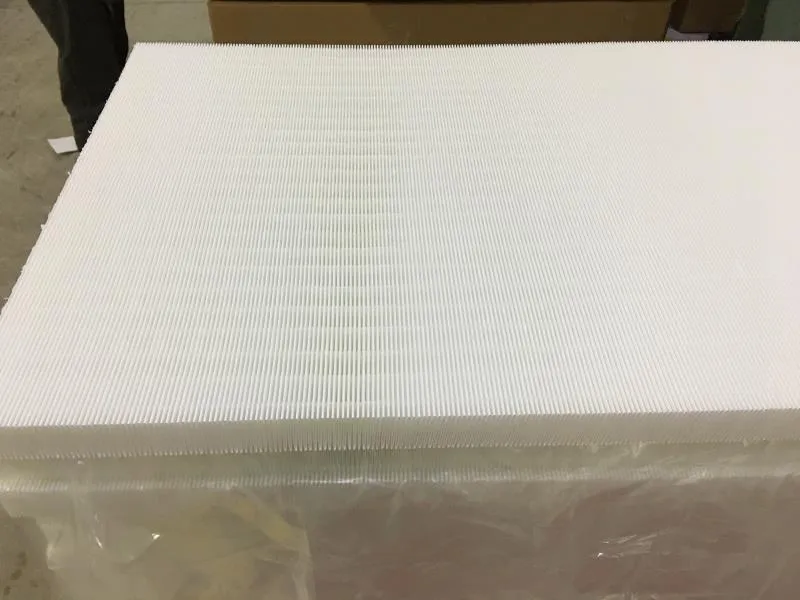
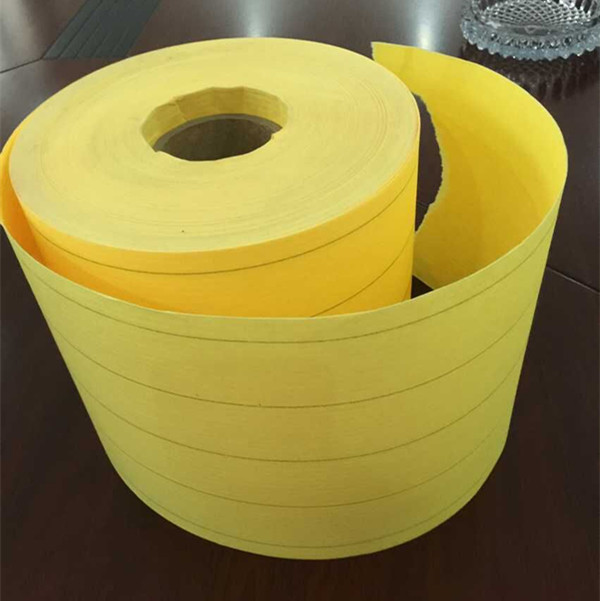
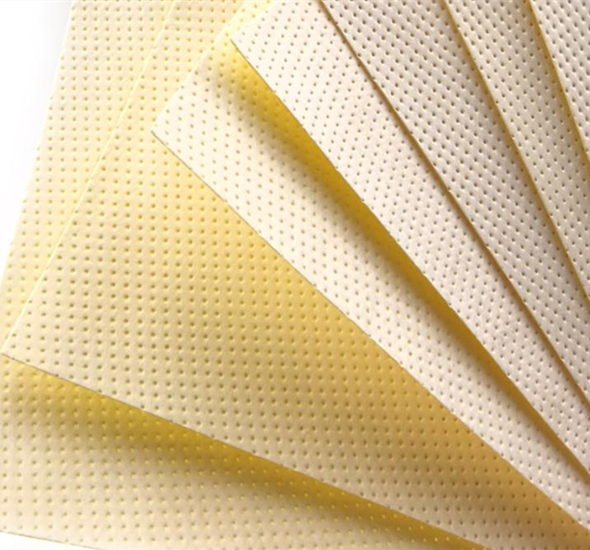
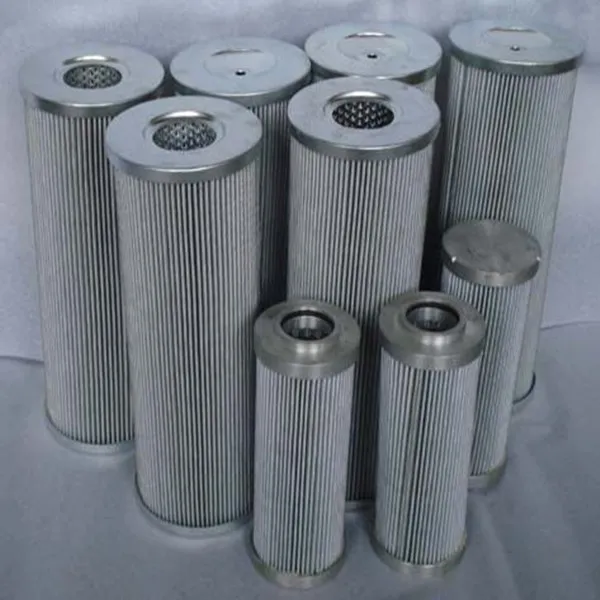
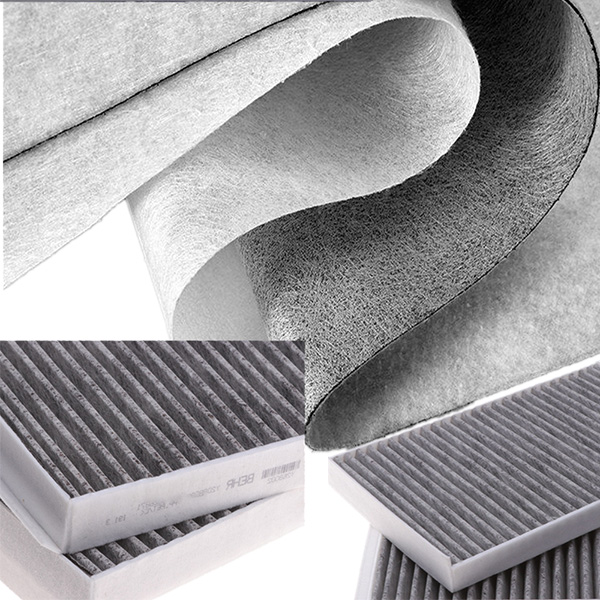
Filter Media nonwoven
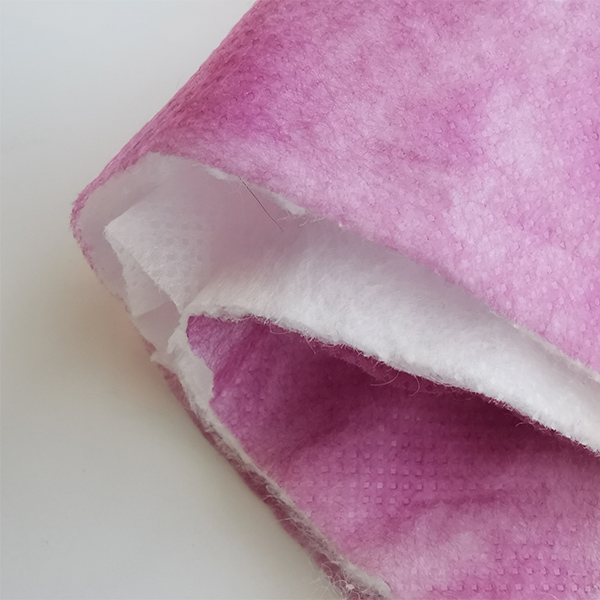
Nonwoven Filter Media is a versatile filtration material engineered from synthetic or natural fibers bonded together through mechanical, thermal, or chemical processes rather than weaving. This structure creates a porous, three-dimensional network with controlled density and pore distribution, enabling efficient capture of particles, dust, and contaminants while maintaining optimal airflow or liquid permeability.
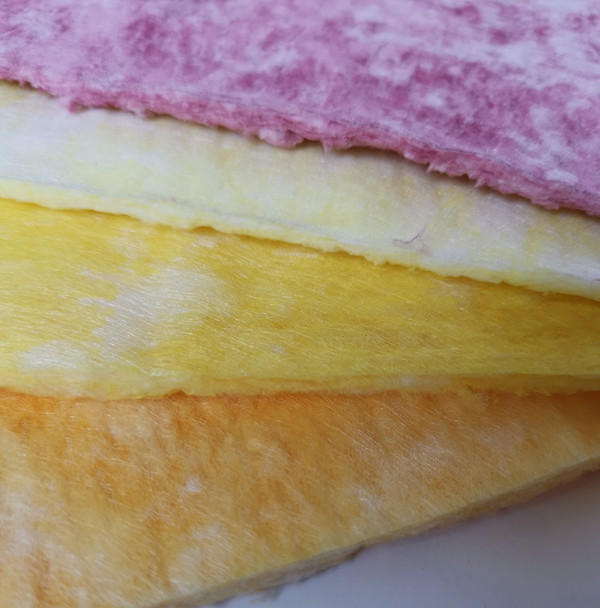
Compared to traditional woven fabrics or paper-based media, nonwoven filters offer superior durability, moisture resistance, and customizable filtration efficiency—ranging from coarse prefiltration to fine sub-micron particle retention. Common materials include polypropylene, polyester, and glass fibers, often treated with additives for enhanced electrostatic adsorption, flame retardancy, or chemical stability.
What is Nonwoven Filter Fabric Used For?
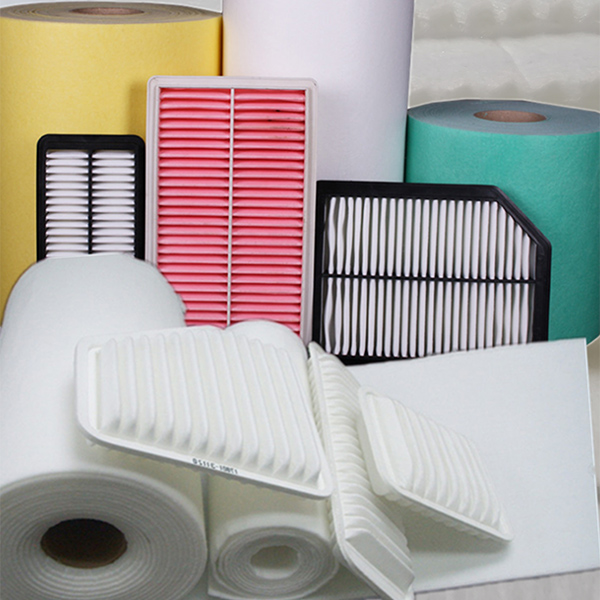
Nonwoven filter fabric is widely used across industries for its versatility and cost-effective filtration capabilities. In HVAC systems, it serves as pre-filters and final filters to capture dust, pollen, and airborne particles, improving indoor air quality. The automotive industry relies on nonwoven media for cabin air filters and engine intake systems to protect against contaminants. Medical applications include surgical masks, respirators, and sterile filtration due to its ability to block microbes while maintaining breathability. Industrial uses range from liquid filtration in water treatment to baghouse filters for dust collection in manufacturing plants. Its customizable density and fiber composition allow tailored solutions for specific filtration needs, from coarse particle removal to high-efficiency sub-micron filtration in critical environments.
Nonwoven Filter Media vs Woven and Meltblown Filter Media
Nonwoven filter media differs from woven and meltblown alternatives in structure and performance. Unlike woven fabrics, which have a rigid, grid-like pattern, nonwoven media consists of randomly arranged fibers bonded together, offering better particle capture and higher dirt-holding capacity. While meltblown media excels in fine filtration (like in masks), it often lacks the mechanical strength of nonwoven fabrics, which combine multiple layers for durability. Nonwoven filters balance airflow and efficiency more effectively than woven screens, which primarily sieve large particles. Additionally, nonwoven media can be engineered with blended materials (e.g., synthetic and natural fibers) for specific chemical or temperature resistance, whereas meltblown media is typically limited to thermoplastics like polypropylene.
High-Temperature and Chemical-Resistant Nonwoven Filter Media
High-performance nonwoven filter media is engineered to withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive environments. Materials like aramid, PTFE, or fiberglass are used for applications exceeding 200°C, such as exhaust gas filtration or metal processing. These fibers resist thermal degradation without losing structural integrity. For chemical resistance, polypropylene or PPS (polyphenylene sulfide) nonwoven media are preferred in acid/alkaline filtration, such as in chemical manufacturing or wastewater treatment. The media’s inert properties prevent reactions with aggressive solvents, ensuring long-term durability. Specialty coatings can further enhance resistance to moisture, oils, or UV exposure. Such robust nonwoven filters are critical in industries like pharmaceuticals, oil refining, and power generation, where both filtration efficiency and material stability are paramount under harsh operating conditions.