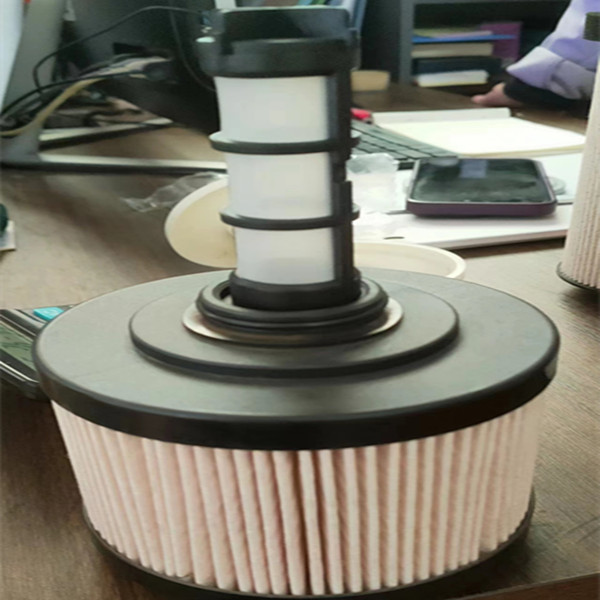
Glass Microfiber Air Filter Paper: Field Notes, Specs, and Real-World Picks
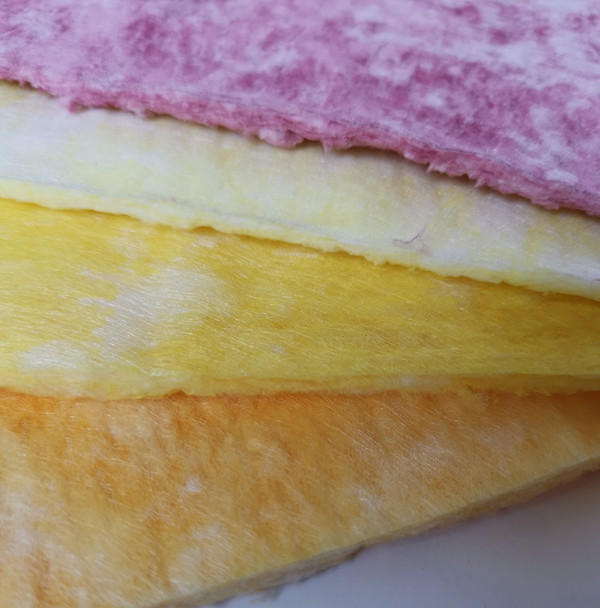
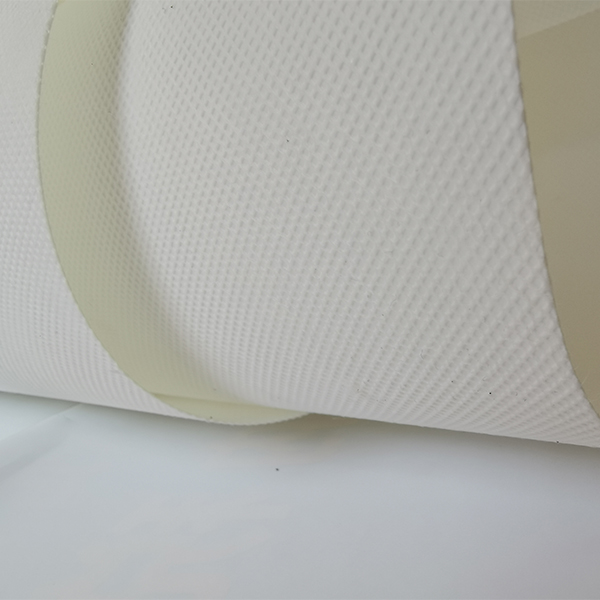
When people ask me what’s quietly powering cleaner air in labs, cleanrooms, and even stack sampling rigs, I often point to the humble glass fiber filter. It’s not flashy. But it’s reliable, tunable, and—if you pick the right vendor—surprisingly consistent batch to batch. This piece looks at the current state of the category, with a close-up on Glass Microfiber Air Filter Paper produced in Hebei, China (No.580 Gongnong Road, Shijiazhuang City 050000, Hebei, P.R. China). Short version: high dust holding capacity, low air resistance, and high filtration efficiency—yes, the brochure points are true, and in many plants I visit, they’re actually borne out.

Industry trends I keep seeing
- Semiconductor and pharma demand is still driving HEPA/ULPA upgrades (EN 1822 / ISO 29463).
- Data centers are chasing lower ΔP to curb fan energy—every Pascal matters.
- Emissions monitoring and life sciences labs prefer binder-free media for low background and non-shedding behavior.
- To be honest, lead times and MOQ flexibility often decide the PO, not just specs.

How the media is made (short process flow)
Materials: borosilicate glass microfibers (sub-micron to a few microns), optional resin binders; sometimes a micro-pleatable scrim.
Method: wet-laid dispersion → sheet formation → dewatering → oven drying → (optional) calendering → thermal curing → roll slitting and QC.
Testing: efficiency and MPPS by EN 1822 / ISO 29463; gravimetric loading and ΔP per ASHRAE 52.2; sodium chloride aerosol per ASTM D2986; ISO 16890 for general ventilation where applicable.
Service life: in HVAC HEPA, roughly 6–18 months depending on prefiltration and final resistance (often 250–450 Pa). In stack sampling or lab capture, it’s per test cycle—hours to days.
Industries: pharma/biotech, microelectronics, hospitals, analytical labs, emissions monitoring, compressor intake in clean applications.

Typical specifications (media-level)
| Parameter | Typical Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Basis weight | 50–120 g/m² | Customizable; affects ΔP and capacity |
| Thickness | 0.3–0.9 mm ≈ | Measured uncompressed |
| Initial ΔP (5.3 cm/s) | 100–180 Pa ≈ | Real-world use may vary |
| Efficiency @ MPPS | H10–H14 (EN 1822) | Dependent on grade |
| Temp resistance | Up to ~250–300°C (binder-free) | Lower with resin systems |
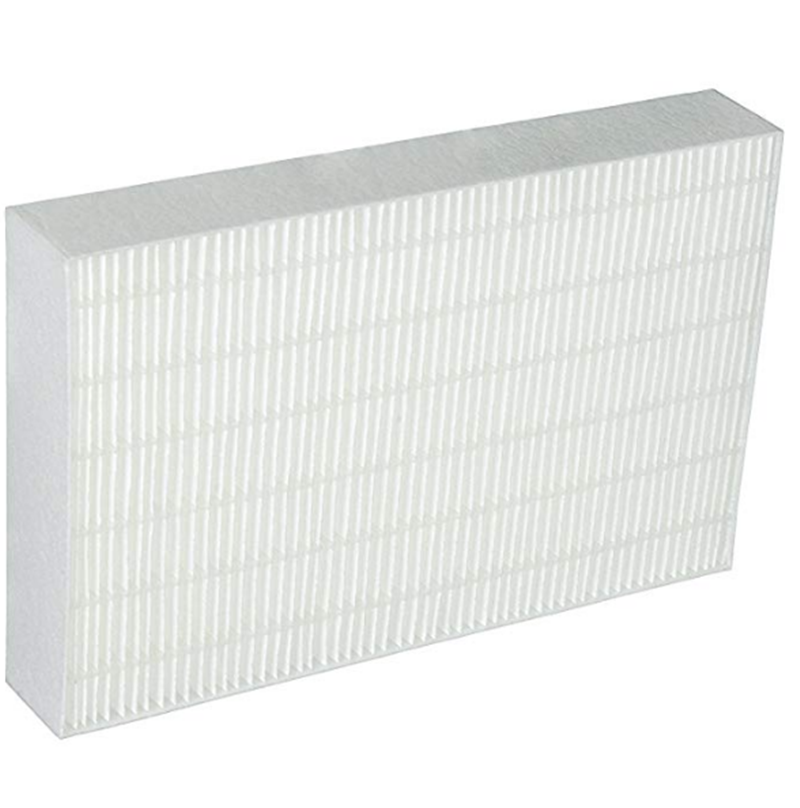
Advantages many customers mention: truly high dust holding capacity, impressively low air resistance for the capture class, and steady roll uniformity. I guess that’s why the glass fiber filter remains the go-to in high-consequence air streams.
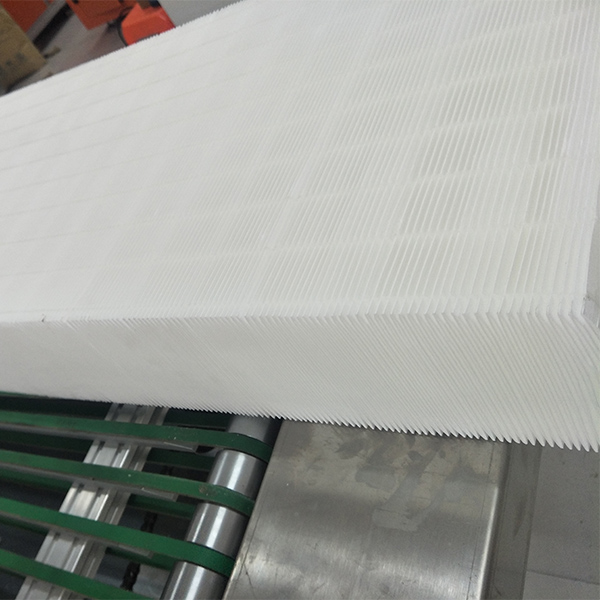

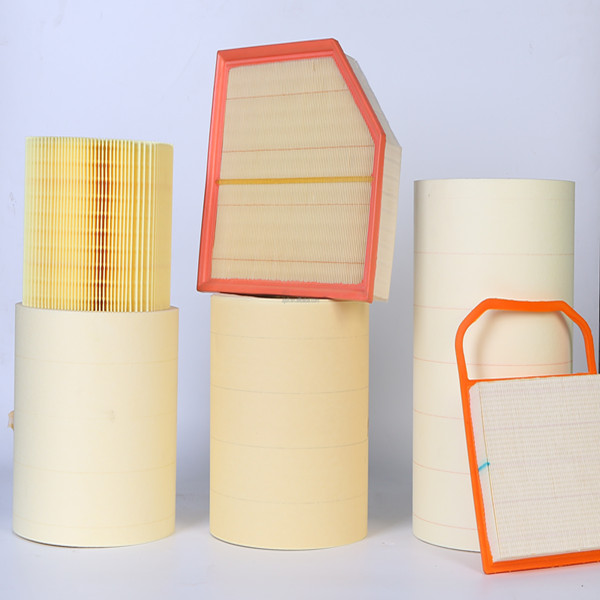
Applications and usage notes
- HEPA/ULPA panels for cleanrooms (H13–H14).
- Sampling filters in emission stacks; low-ash, low background mass helps.
- Biosafety cabinets and isolators—where resin-free grades can reduce VOC risk.
- General ventilation upgrades (ISO 16890 ePM1 media, where appropriate).
Tip: watch pleat geometry and sealants; the best glass fiber filter media can be let down by poor potting.

Vendor comparison (high-level)
| Vendor | Certifications | Lead Time | Customization | Price Range ≈ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hebei producer (Glass Microfiber Air Filter Paper) | ISO 9001; grades for EN 1822 | 2–5 weeks | Basis weight, binder %, roll width | Mid |
| EU-based media maker | ISO 9001/14001; EN 1822 | 4–8 weeks | Wide portfolio incl. ePTFE laminates | High |
| US-based specialty paper | ISO 9001; ASTM focus | 3–6 weeks | Small-lot R&D runs | Mid–High |
Customization quick list
Basis weight and thickness; binder-free vs. resin-bonded; hydrophobic treatment; roll width up to 1.2–1.5 m ≈; pleatability tuning; test certificates (EN 1822 scan, ISO 16890 classification, ASTM D2986 data). That’s usually enough to tailor a glass fiber filter to your line.

Mini case notes
- Pharma fill line isolator: switching to binder-free H14 media cut VOC background by ~30% and maintained ≥99.995% @ MPPS.
- Semiconductor subfab: optimized basis weight reduced initial ΔP by ~18%, saving fan energy (small, but constant).
- Stack monitoring lab: low-ash glass fiber filter improved gravimetric precision; blanks stabilized faster in the desiccator.
Final thought
Specs matter, but consistency and documentation matter more. Ask for recent lot test sheets, and verify to your standard. It seems obvious, yet it’s where the best programs win.
Authoritative citations
- ISO 16890: Air filters for general ventilation.
- EN 1822-1:2019 / ISO 29463: High efficiency air filters (EPA, HEPA, ULPA).
- ASHRAE Standard 52.2: Method of Testing General Ventilation Air-Cleaning Devices.
- ASTM D2986: Standard Test Method for Airflow Resistance and Dust Capacity of Air Filter Media.
- GB/T 14295: Air filters—General specification (China).
Post time: Oct-19-2025