ಸೆಲ್ಯುಲೋಸ್ ಫಿಲ್ಟರ್ ಪೇಪರ್
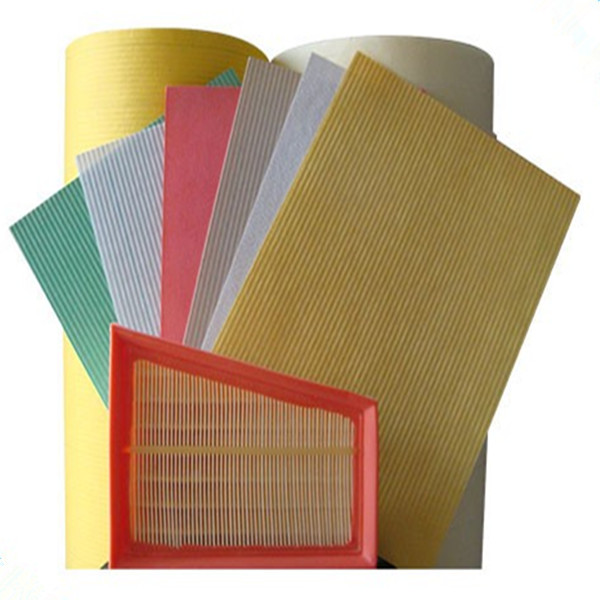
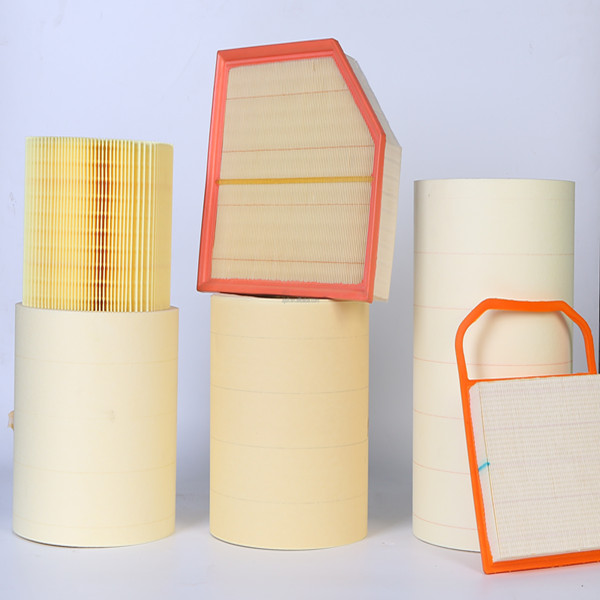
Cellulose filter paper is a highly porous, pure fibrous material made primarily from plant-derived cellulose. It is widely used in laboratories for filtration, separation, and analytical processes due to its excellent wet strength, retention capabilities, and compatibility with various solvents. The paper's fine mesh structure allows it to trap particles while permitting liquids or gases to pass through efficiently.
Available in different grades, cellulose filter paper varies in thickness, pore size, and filtration speed to suit specific applications, such as qualitative or quantitative analysis. Common applications include air and liquid filtration, sample preparation in chromatography, and residue analysis in environmental testing. Its biodegradability and cost-effectiveness also make it an environmentally friendly choice. Some specialized types are ashless or acid-treated for high-precision analytical work.
What is the use of cellulose filter paper?
Cellulose filter paper is primarily used for separating solids from liquids or gases by filtration. Its porous structure allows liquids or gases to pass through while retaining solid particles, making it essential in various scientific and industrial processes. In laboratories, it is commonly used for qualitative and quantitative analysis, such as collecting precipitates, clarifying solutions, or performing gravimetric analysis.
The paper's ability to retain particles of specific sizes depends on its pore size, which can range from coarse to fine. Additionally, cellulose filter paper is used in air monitoring to capture particulate matter for environmental or occupational health studies. Its high purity and chemical compatibility with many solvents make it suitable for use in chemical, biological, and pharmaceutical applications. In industrial settings, it aids in processes like wastewater treatment, oil purification, and food and beverage production. Its affordability, disposability, and efficiency make it a versatile tool across multiple fields.
What are cellulose filter papers made of?
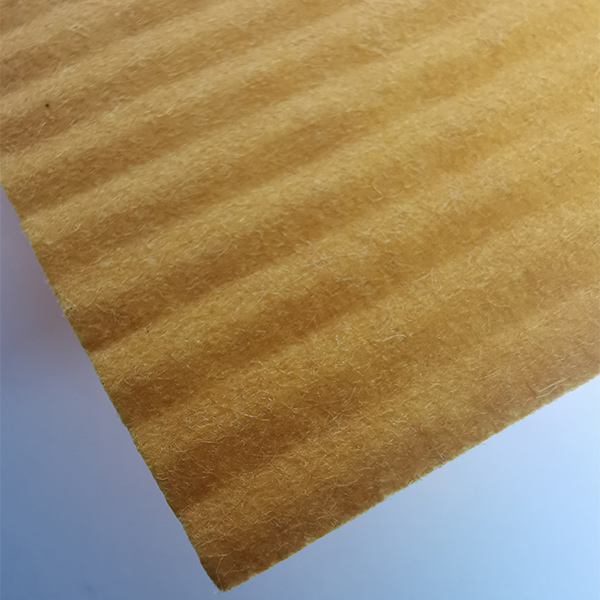
Cellulose filter papers are composed primarily of highly purified cellulose fibers derived from plant sources, such as cotton or wood pulp. These fibers are processed to remove impurities like lignin, resins, and other non-cellulosic components, resulting in a material with high chemical purity and consistent performance. The fibers are then formed into sheets through a wet-laying process, where they are suspended in water and pressed into thin, uniform mats.
The paper's porosity and pore size are controlled during manufacturing by adjusting fiber length, bonding, and compression. Some filter papers may include additives like binders or wet-strength agents to enhance durability or resistance to specific chemicals. The final product is inert, biodegradable, and compatible with a wide range of solvents and reagents, making it ideal for laboratory and industrial use. The purity and structure of cellulose fibers ensure minimal contamination, which is critical for sensitive applications like analytical chemistry or microbiological testing.
Applications of cellulose filter paper in laboratory and industrial settings
In laboratories, cellulose filter paper is widely used for analytical procedures, including sample preparation, particle separation, and chromatography. It is essential in gravimetric analysis, where precipitates are collected and weighed, and in qualitative tests to identify substances based on filtration properties. In microbiology, it aids in sterilizing liquids or air by trapping microorganisms. Industrial applications include wastewater treatment, where it removes suspended solids, and in the food and beverage industry for clarifying liquids like juices or oils.
The paper is also used in manufacturing processes, such as filtering coatings or lubricants to ensure product quality. In environmental monitoring, cellulose filter paper captures airborne particles for pollution analysis. Its versatility, combined with low cost and disposability, makes it indispensable in both research and large-scale production. The paper's ability to be customized for specific pore sizes and chemical resistances further expands its utility across diverse fields.