If you work anywhere near filtration, you’ve probably heard someone ask for a [filter making machine]. I get it—machines that pleat, cut, bond, and assemble filter elements are the unsung heroes behind clean rooms, clean cabins, and clean turbines. I’ve been visiting factories from Hebei to Houston and, to be honest, the difference a well-tuned line makes is night and day.
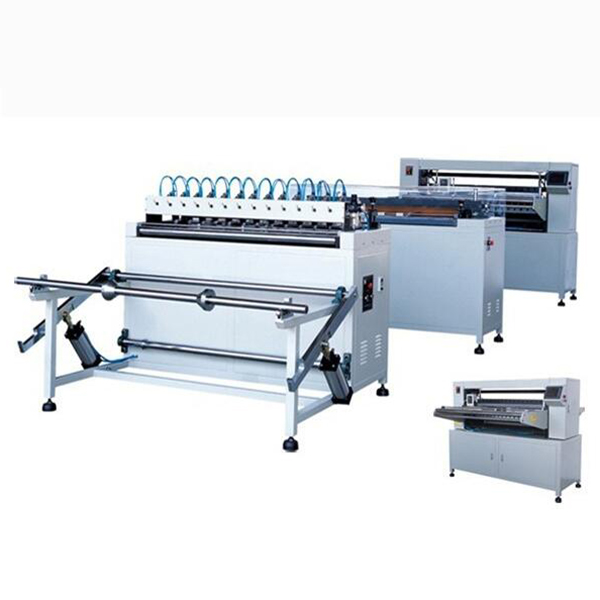

What it does (and why factories swear by it)
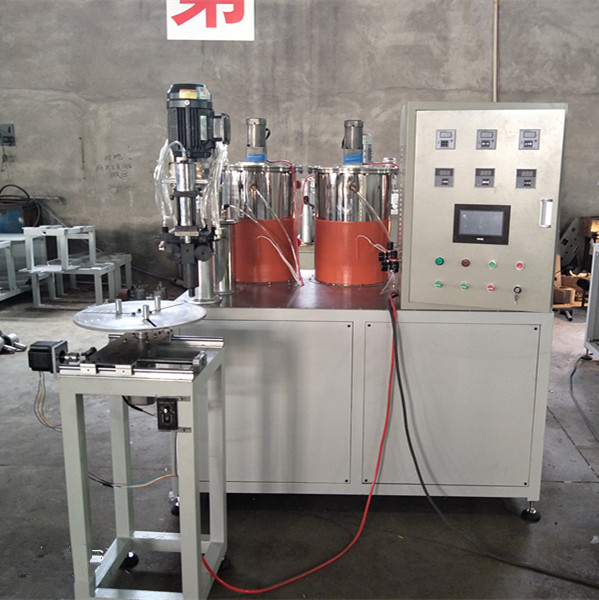
The filter making machine from Anya Filter Media (origin: No.580 Gongnong Road, Shijiazhuang City 050000, Hebei, P.R. China) runs fully or semi-automatically. It keeps pleat height consistent, cuts to length, bonds end caps, and stacks parts with a PLC touchscreen that operators actually like—surprisingly rare. It works with filter paper, nonwoven, fiberglass, even mesh. Many customers say they switched for the speed; others stayed for the uptime.
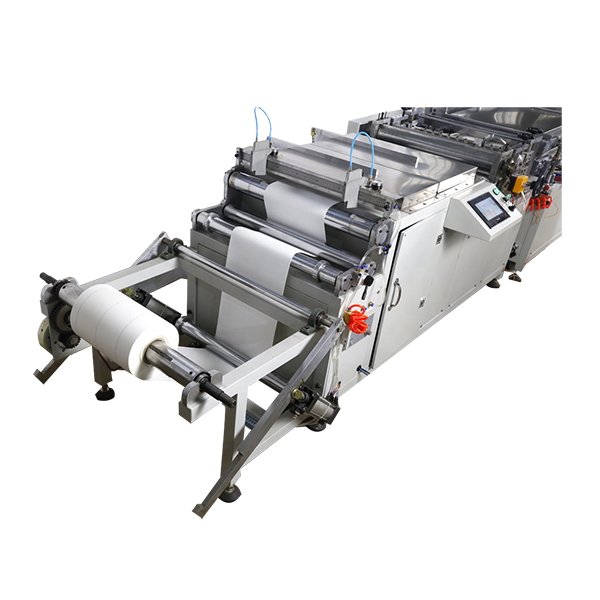

Process flow (real shop-floor steps)
- Material loading: paper/nonwoven/fiberglass rolls checked for GSM and moisture.
- Pleating: hot-melt or blade pleating; typical height 10–75 mm with ±0.2 mm tolerance.
- Stabilization: curing/cooling tunnel for pleat memory.
- Cutting and edge sealing: rotary or guillotine; PU/hot-melt bonding as needed.
- Core wrapping/mesh insertion: for oil and hydraulic types.
- End cap assembly: PU potting or metal crimp, depending on spec.
- Testing: pressure drop, burst strength, leak test, and dimension check.
Standards used on lines I’ve seen: ISO 16890 for air filters, EN 1822 for HEPA/ULPA, and ASHRAE 52.2 for MERV ratings. Automotive clients often ask for IATF 16949 documentation on traceability.
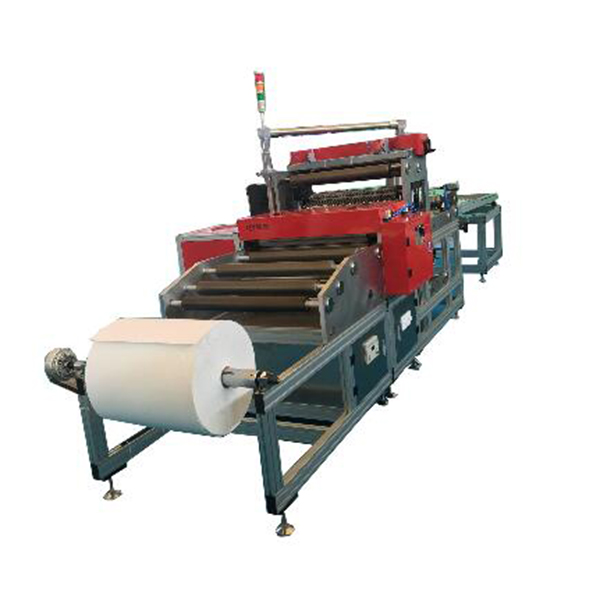

Product specifications (typical configuration)
| Operation Modes | Fully-auto or Semi-auto (switchable modules) |
| Materials | Paper, nonwoven, fiberglass, mesh |
| Pleat Height Range | ≈10–75 mm (real-world may vary by media) |
| Line Speed | Up to ~25 m/min or 18–40 pcs/min (format dependent) |
| Accuracy | Pleat pitch ±0.2 mm; length cut ±0.5 mm |
| Control | PLC + touchscreen HMI, recipe storage, OEE counter |
| Power/Air | 380V/50Hz (others optional); 0.6–0.8 MPa compressed air |
Service life: many lines run 3 shifts with annual preventive maintenance; critical rollers last ~2–4 years, depending on media abrasiveness.
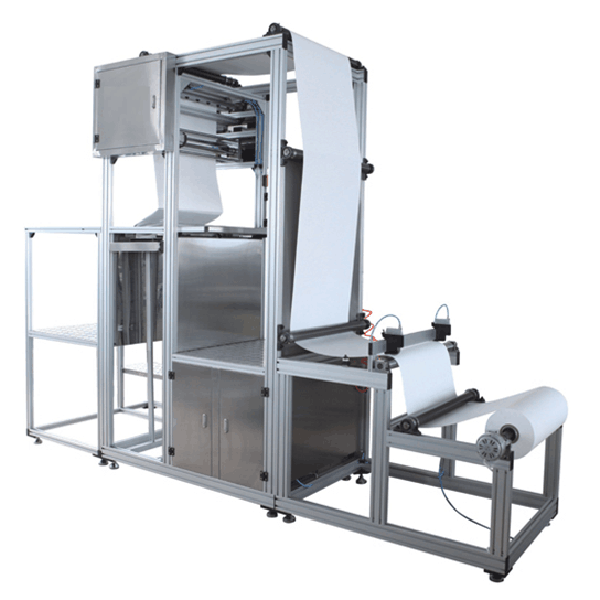

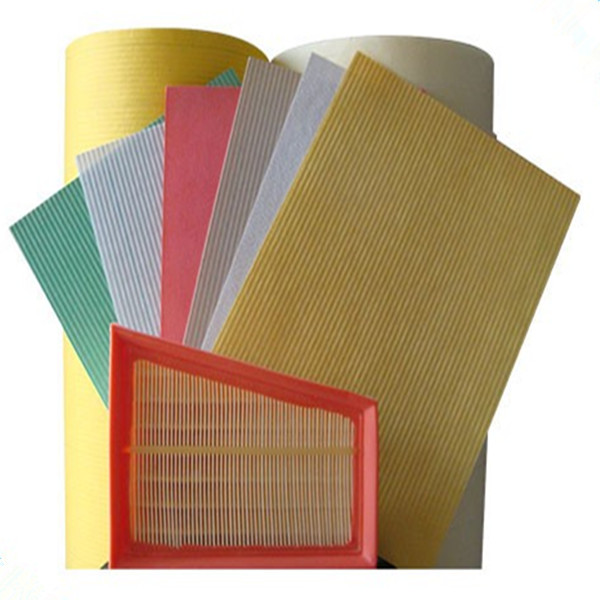
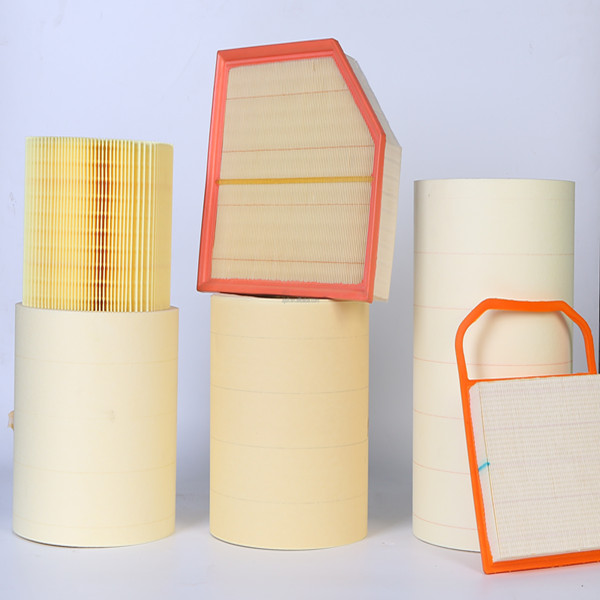
Applications and results
Use cases include HEPA/HVAC plants, automotive oil/cabin filter shops, and industrial dust cartridges. One mid-size HVAC client switched to the filter making machine for fiberglass pleating; pressure-drop scatter tightened by 18% and scrap fell below 1.5%—not a lab miracle, just better control.
Vendor snapshot (field notes)
| Vendor | Strengths | Lead Time | After‑sales |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anya Filter Media | Accurate pleating, wide media support, friendly HMI | ≈6–10 weeks | Remote PLC support + onsite training |
| Vendor B | High throughput; pricier tooling | 8–12 weeks | Ticket-based, slower onsite |
| Vendor C | Good for entry-level lines | 10–14 weeks | Limited global coverage |
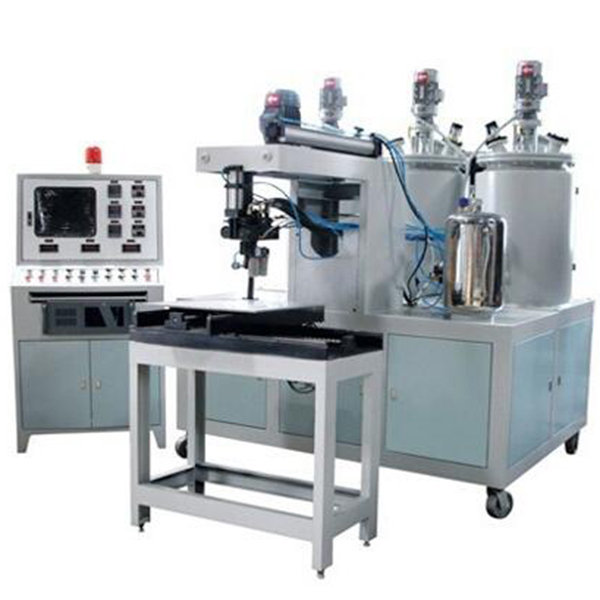

Customization and compliance
Custom fixtures for odd pleat geometries, HEPA edge sealing, and cabin filter PU potting are common. PLC recipes lock down MERV or EN 1822 settings. CE safety guards are standard; UL electrical packages on request. For automotive, IATF 16949 documentation can be aligned with your PPAP flow.
Test data snapshot
- HEPA module: ≥99.97% @ 0.3 μm; leak ≤0.01% per EN 1822-4 (line average, n=30).
- HVAC MERV 13: initial ΔP ≈ 95–105 Pa @ 0.944 m/s (ISO 16890 bench).
- Burst strength: >350 kPa for oil filter cores (fixture test, room temp).
Note: values are indicative; media lots and curing profiles matter a lot, actually.

Bottom line
If you need repeatable pleats, clean seals, and a sane operator interface, this filter making machine is a solid, no‑drama choice. It’s fast, adaptable, and doesn’t fight you on maintenance.
Authoritative citations
Post time: Oct-16-2025